Question 1. Multiple choice questions:
(i) Which one of the following minerals is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass of weathered materials?
(a) Coal (b) Bauxite
(c) Gold (d) Zinc
(ii) Koderma in Jharkhand is the leading producer of which one of the following minerals?
(a) Bauxite (b) Mica
(c) Iron ore (d) Copper
(iii) Minerals are deposited and accumulated in the strata of which of the following rocks?
(a) Sedimentary rocks (b) Metamorphic rocks
(c) Igneous rocks (d) None of the above
(iv) Which one of the following minerals is contained in the Monazite sand?
(a) Oil (b) Uranium
(c) Thorium (d) Coal
Answer 1
(i)—(a),
(ii)—(b),
(iii)—(a)
(iv)—(c).
Question 2. (i) Answer the following questions in about 30 words:
(a) Distinguish between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
(b) Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
(ii) What is a mineral?
(iii) How are minerals formed in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
(iv) Why do we need to conserve mineral resources?
Answer 2 (a) Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
| Ferrous minerals | Non-ferrous minerals |
| Minerals containing iron are called ferrous minerals. | Minerals which do not contain iron are called non-ferrous minerals. |
| For ex: iron ore and manganese. | For ex: bauxite, lead and gold. |
(b) Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy.
| Conventional sources | Non-conventional source |
| Conventional sources of energy are generally exhaustible and polluting. | Non – conventional sources of energy are usually inexhaustible and non- polluting. |
| For Ex: firewood, coal and petroleum. | For ex: solar, wind, tidal and atomic energy. |
(ii) Mineral is a homogenous, naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure. They are formed by a combination of elements. They are an essential part of our lives. The hardest mineral is diamond and the softest is talc. Minerals are usually found in “ores”.
(iii) In igneous and metamorphic rocks, minerals may occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints. The smaller occurrences are known as veins and the larger are known as lodes. In most cases, they are formed when minerals in liquid/molten and gaseous forms are forced upwards through cavities towards the earth’s surface. They cool and solidify as they rise.
(iv) We need to conserve mineral resources because they are finite and non-renewable. Rich mineral deposits are our country’s most valuable but short-lived possessions. Continued extraction of ores leads to increasing costs as mineral extraction comes from greater depths along with decrease in quality.
Question 3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Describe the distribution of coal in India.
(ii) Why do you think that solar energy has a bright future in India?
Answer 3 (i) Coal is an important fossil fuel of India. It is the most abundantly available fossil fuel. It provides about 80% of the nation’s energy needs. India is highly dependent on coal for meeting its commercial energy requirements. In India, coal occurs in rock series of two main geological ages—Gondwana and tertiary. While Gondwana coal is about 200 million years old, tertiary deposits are approximately 55 million years old. The major resources of Gondwana coal which are metallurgical coal, are located in the Damodar valley (West Bengal, Jharkhand). Jharia, Raniganj and Bokaro are important coalfields. The Godavari, Mahandi, Son and Wardha valleys also contain coal deposits. Tertiary coals occur in the north-eastern states of Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
(ii) Being a tropical country, India has an abundance of sunlight. Hence, there are huge possibilities of tapping solar energy. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. Solar energy is becoming popular in rural and remote areas. Use of solar energy will be able to minimise the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes, which in turn will contribute to environmental conservation and adequate supply of manure in agriculture. Solar energy is a nonconventional source of energy and also eco-friendly. The largest solar plant of India is located at Madhapur, near Bhuj (Gujarat) where solar energy is used to sterlise milk cans.
Activity
Fill the name of the correct mineral in the crossword below:
DOWN
1. Found in placer deposit (4)
2. Iron ore mined in Bailadila (8)
3. Indispensable for electrical industry (4)
4. Geological Age of coal found in north east India (8)
5. Formed in veins and lodes (3)
ACROSS
1. A ferrous mineral (9)
2. Raw material for cement industry (9)
3. Finest iron ore with magnetic properties (9)
4. Highest quality hard coal (10)
5. Aluminium is obtained from this ore (7)
6. Khetri mines are famous for this mineral (6)
7. Formed due to evaporation (6)
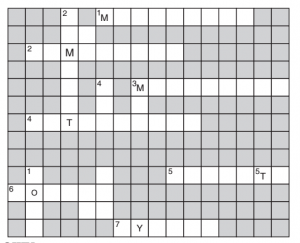
Answer
DOWN
1. Rock
2. Hematite
3. Coal
4. Tertiary
5. Tin
ACROSS
1. Manganese
2. Limestone
3. Magnetite
4. Anthracite
5. Bauxite
6. Copper
7. Gypsum