Question 1. Multiple choice questions.
(i) Which one of the following type of resource is iron ore?
(a) Renewable (b) Biotic
(c) Flow (d) Non-renewable
(ii) Under which of the following type of resource tidal energy cannot be put?
(a) Replenishable (b) Human-made
(c) Abiotic (d) Non-recyclable
(iii) Which one of the following is the main cause of land degradation in Punjab?
(a) Intensive cultivation (b) Deforestation
(c) Over irrigation (d) Overgrazing
(iv) In which one of the following states is terrace cultivation practised?
(a) Punjab (b) Plains of Uttar Pradesh
(c) Haryana (d) Uttarakhand
(v) In which of the following states black soil is predominantly found?
(a) Jammu and Kashmir (b) Maharashtra
(c) Rajasthan (d) Jharkhand
Answer 1
(i) (d) Non-renewable
(ii) (a) Replenishable
(iii) (c) Over irrigation
(iv) (d) Uttarakhand
(v) (b) Gujarat
Question 2. Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(i) Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
(ii) What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
(iii) What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
(iv) What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
Answer 2 (i) Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh are the states having black soil. The crop which is mainly grown in this soil is cotton. This soil is also called ‘Regur’ or black cotton soil.Other crops which can be grown in black soil are rice, sugarcane, wheat, Jawar, linseed.
(ii) The river deltas of the eastern coast have alluvial soil.
Three features of alluvial soil:
1) Alluvial soils are very fertile.
2) Alluvial soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt and clay..
3) These soils contain ample amount of phosphoric acid, potash and lime so they are ideal for growing sugarcane, wheat and paddy.
(iii) In hilly areas, soil erosion can be controlled by contour which refers ploughing across contour-lines, making use of terrace farming techniques and using strips of grasses to check soil erosion by wind and water.
(iv) Biotic Resources: The resources which are obtained from the biosphere, from forest and the materials derived from them and have life are called Biotic Resources.
For example, animals and plants including human beings.
Abiotic Resources: The resources which are composed of non-living things are called Abiotic Resources.
For example rocks ,water, minerals, metals, wind, solar
Question 3. Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(i) Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since 1960-61?
(ii) How have technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Answer 3 (i) Land resources in India are primarily divided into agricultural land, forest land, pasture and grazing land, and waste land. Waste land includes rocky, arid and desert areas, and land used for non-agricultural purposes like housing, roads, industry.According to the recent data, about 54% of the total land area is cultivable or fallow, 22.5% is covered by forests and 3.45% is used for grazing. The rest is wasteland, with traces of miscellaneous cultivation.The land under forest has not increased since 1960–61 because in the post-independence era demand for more land to expand agriculture, mainly after Green Revolution, developmental works and infrastructural facilities, led to clearance of forests areas. Industrialisation and urbanisation also decreased the forest area.
(ii) Technical and economic development has led to more consumption of resources on account of various factors such as:
1) Technological development provides sophisticated equipment. As a result, production increases ultimately leading to consumption of more resources. Technological advancement leads to the conversion of more natural resources into useful resources thus the consumption also increases.
2) Technological development also leads to economic development. When the economic condition of a country rises, the needs of people also rise. It again results in more consumption of resources.
3) Economic development provides favourable environment for the development of latest technologies. It helps to make or convert various materials found around us into resources. Finally, it results in the consumption of newly available resources too.
PROJECT/ACTIVITY
Question 4. Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
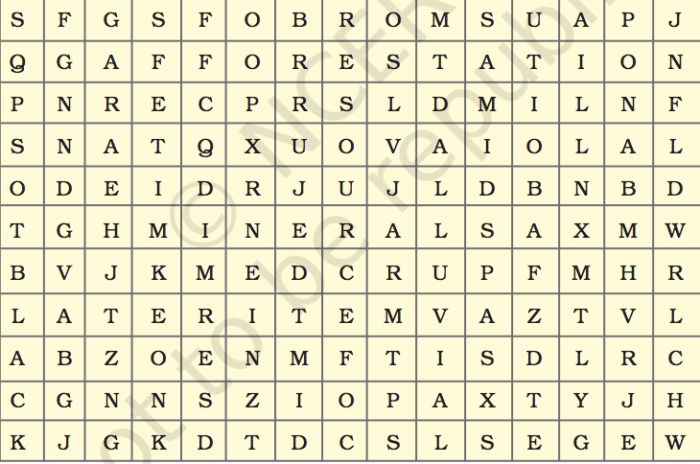
(i) Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals.
(ii) A type of non-renewable resource.
(iii) Soil with high water retaining capacity.
(iv) Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate.
(v) Plantation of trees on a large scale to check soil erosion.
(vi) The Great Plains of India are made up of these soils.
Answer 4 (i) Resources
(ii) Minerals
(iii) Black
(iv) Laterite
(v) Afforestation
(vi) Alluvial