DAV Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Solutions: Are you looking for DAV Class 8 Science Books Chapter 1 Solutions then you are in right place , we have discussed the solution of Science class 8 book Chapter 1 The Cell – Its Structure and Functions. These DAV Solutions will assist you in learning about the concept of a cell, its parts, different types and parts of cells, the nucleus, animal cells, plant cells, and the differences between plant and animal cells.
DAV CLASS 8 The Cell – Its Structure and Functions Question and Answer
A. Fill in the blanks.
Fill In The Blanks
1)All Living organisms are made up of Cells.
2)The Cell Wall Provides rigidity and protection to the plant cell.
3) All Cellular activities are controlled by the Nucleus.
4) The Mitochondria is also Known as the Powerhouse of the cell.
5)Tissue is a group of cells performing a specific function.
6)He was Robert Hooke who observed cells for the first time.
B. Match the following:
(I)Golgi Complex ——— Packaging Center
(II) Ribosomes————-protein Synthesis
(III) Chromosomes ——–Genes
(IV)Dead Cells ————-Cork
(V)Photosynthesis——– Chloroplast
C. Tick (√) The Correct Option.
1) The cell organelle which act as a storage bag for a cell, is known as the:-
1. Chloroplast 2. Chromoplast
3. Mitochondria 4. Vacuole
Ans: Vacuole
2) Hen’s egg is :-
1. a cell organelle 2. a tissue
3. a single cell 4. an organ
Ans: Single Cell
3) The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by the :-
1. Cytoplasm 2. nuclear membrane
3. cell membrane 4. protoplasm
Ans: Nuclear Membrane
4)Which of the following will not be found in an egg cell, human liver cell and an Amoeba?
1. ribosomes. 2. cell membrane
3. Mitochondria 4. Cell Wall
Ans: Cell Wall
5)Which of the following represent the correct sequence?
1. tissue -> cell -> organ -> organ some
2.organ -> tissue -> organ system -> cell
3. cell -> organ -> tissue -> organ system
4. Cell -> tissue ->organ ->organ system
Ans: Cell -> tissue ->organ ->organ system
6) Which amongst the following pairs, can be found only in a plant cell but not in an animal cell ?
1. cell wall and plastids
2. plastids and cilia
3. cell wall and cell membrane
4. plastids and mitochondria
Ans :cell wall and plastids
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
1. List the (main) factors that determine the shape of a cell.
Ans: Location and function are the (primary) factors that determine the shape of a cell.
2.Distinguish between unicellular and multicellular organisms. Give two examples of each.
Ans:
| Unicellular organisms are made up of a single cell | Multicellular organisms are made up of many cells. |
| Bacteria and Amoeba. | Humans and Cockroach. |
3.Give reasons for the following:
(a) The cell is called the structural and functional unit of life. (b) Plant cells are more rigid than the animal cells.
(a) Ans: All organisms are made up of cells. A cell is capable of independent existence. Due to this, cell is called the structural and functional unit of life.
(b)Ans: Cell wall is present in plant cell. Due to this, plant cells are more rigid than animal cells.
4.Which cell organelle is known as the ‘Powerhouse of the cell? Why is it so called?
Ans: Mitochondria is known as the Powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria are the site of cellular respiration. Energy is produced during this process. Due to this, mitochondria are called the Powerhouse of the cell.
5.Name the cell organelles responsible for imparting colour to the leaves and fruits of a plant.
Ans: Chromoplast is responsible for imparting colour to fruits. Chloroplast is responsible for imparting colour to the leaves.
6.What are cilia and flagella? Write one similarity and one dissimilarity between the two of them.
Ans: Cilia and flagella are extensions on the cell membrane which help in locomotion and collection of food in organisms like Amoeba and Paramoecium. Cilia are much smaller than flagella.
7.If onion peel cells and cheek cells are observed through a microscope, state the two major differences that the observer is likely to find.
Ans: Two Major differences that the observer is likely to find are:
| In Onion peel cells | In Cheek cells |
| Cells are arranged in rows. | Cells randomly arranged. |
| Cell wall is present. | Cell wall is absent. |
8.Classify the following into cells, tissue and organ.
skin, fat cell, RBC, blood, ear, muscle
| Cell | Fat cell and RBC. |
| Tissue | Blood and muscle. |
| Organ | Skin and ear. |
E. Answer the following questions.
1. “All cells in an organism do not have the same shape.”
Justify the above statement by drawing at least three different cell types found in human beings.
Ans: Three different cell types which are found in human beings are as follows :
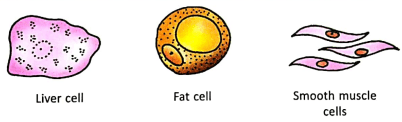
The liver cell is irregular in shape, the fat cell is spherical, and the muscle cell is spindle-shaped, as seen in the diagrams above. This demonstrates that not all cells in an organism are the same shape.
2. Where, and how, are chromosomes formed? State their significance.
Ans:During cell division, chromosomes are generated in the nucleus. The chromatin (in the nucleus) condenses to form thicker, thread-like chromosomes when the cell is ready to divide. Character inheritance is determined by chromosomes, which are passed down from generation to generation.
3. With the help of well labelled diagrams, highlight three differences between a plant cell and an animal cell.
Ans: Three differences between a plant cell and an animal cell are:
| Plant Cell | Animal cell |
| Cell wall is present. | Cell wall is absent. |
| Chloroplast is present. | Chloroplast is absent. |
| Vacuole a very large. | Vacuoles are small. |
4. Write the functions performed by the following cell organelles.
Ans:
(a) Endoplasmic Reticulum- It provides channels for transport of materials in a cell.
(b) Golgi Complex-They are responsible in the processing and packaging of materials produced by the cell.
(c) Nucleus- A specialized structure in the cells, bound by the nuclear membrane; responsible for controlling the function of all cellular activities.
(d) Chromoplasts- Chromoplast is responsible for providing colour to the plants.
(e) Vacuoles- Vacuoles act as storage sac of the cell. It stores excess of water and waste products.
(f) Mitochondria- These are rod-shaped or spherical structures. They are responsible for cellular respiration and for generation of energy for different activities of life.
5. The cell membrane is a very important component of a cell. How is damage to the cell membrane likely to impact the functions of the cell?
Ans: When the cell membrane gets damaged, it exposes the cell’s contents to external environment. This results in stoppage of all functions of the cell, and eventually eventually leading to cell death.
6. Define the term ‘cell’, for plants/animals. Name the different organelles that make a cell. Explain why none of these is called the structural and functional unit of life.
Ans: Cell is the fundamental and structural unit of life. Different cell organelles in a plant cell are; nucleus, Golgi complex, mitochondria, chloroplast, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosome, vacuole, and ribosome. None of the cell organelles is capable of independent existence. So, they are not called the structural and functional unit of life.
Other Related Chapters
- Chapter 1 | The Cell – Its Structure and Functions | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 2 | Microorganisms: Friends or Foes | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 3| Metals and Non-Metals| Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 4| Force and Pressure | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 5| Friction | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 6| Sources of Energy | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 7| Combustion | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 8| Conservation of Plants and Animals | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 9| Crop Production and Its Management | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 10| Refraction and Dispersion of Light | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 11| The Human Eye | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 12| Sound | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 13| Synthetic Fibres and Plastics | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 14| Reproduction in Animals | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 15| Reaching the Age of Adolescence | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 16| Electric Current and Its Chemical Effects | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 17| Stars and Solar System | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 18| Earthquakes | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 19 | Pollution of Air | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 20 | Pollution of Water | Class- 8 DAV Science
Upload plzz…
Pls update ques ans also. Pls update fast
nicce