Are you looking for DAV Books Solutions then you are in right place, we have discussed the solution of Science class 6 book Chapter 13 Magnets which is followed in all DAV School. Solutions are given below with proper Explanation please bookmark our website for further updates!! All the Best !!
DAV Class- 6 Magnets Question and Answer
Something To Know
A. Fill in the blanks.
1. The materials which do not get attracted towards a magnet are called non-magnetic materials.
2. The bar magnet is an example of a permanent magnet.
3. Even the smallest piece of a bar magnet has two magnetic poles.
4. Earth has its magnetic north poles towards its geographical south pole.
5. Magnets have been used for various purposes.
B. Write True or False for the following statements.
| Column 1 | Column 2 (True/False) |
| 1. Naturally occurring magnets are called loadstones. | True |
| 2. An aluminium foil would get attracted by a magnet. | False |
| 3. Bar magnets have a ‘north seeking’ pole as well as a ‘south seeking’ pole. | True |
| 4. Two magnetic poles, of the same kind, attract each other. | False |
| 5. When two magnets are moved farther apart from each other, the forces, that attract or repel them, tend to become stronger. | False |
C. Tick the correct option.
1. The magnetic material, that was discovered first of all, is-
Answer 1: loadstone
2. A magnet can attract-
Answer 2: an iron nail
3. A material, that is often used to make a temporary magnet, is-
Answer 3: soft iron
4. When we suspend a bar magnet from a thread, it comes to rest along the-
Answer 4: north-south direction
5. A device, which generally does not use a magnet, is-
Answer 5: a geyser
D. Answers the following questions in brief.
1. State any two properties of a bar magnet.
Answer: Two properties of a bar magnet are-
1. Attractive property: – the magnet is capable of attracting a small piece of iron, steel, etc.
2. Directive property: – a freely suspended magnet always points along the north and south direction.
2. Maximum iron filling stick to the two ends of a bar magnet. Why?
Answer: Maximum iron filling sticks to the ends of a bar magnet because the strength of a bar magnet is maximum near the poles.
3. Suppose we bring the north pole of one bar magnet towards the north pole of another freely suspended bar magnet. What are we likely to observe?
Answer: we observe repulsion when we bring the north pole of one bar magnet towards the north pole of another freely suspended bar magnet.
4. Two magnets, X and Y, are placed as shown in the diagram. It is that magnet X floats above magnet Y. Give reason for this observation.
Answer: Magnet X floats above magnet Y because the two magnets X and Y are having the same poles towards each other.
5. You are given a knitting needle made of steel. How can you make it into a magnet?
Answer: We can make the steel needle into a magnet by placing it near a bar magnet for some time, this is because the needle acquires some magnetism.
E. Answer the following questions.
1. Distinguish between the following:
(a) permanent magnets and temporary magnets.
| Permanent magnets | Temporary magnets |
| These are magnets that once made remain as magnets for a long period of time. | These are magnets that once made remain as a magnet only for a short interval of time. |
| Steel, cobalt steel and alnico are some of the materials that are used for making permanent magnets | Soft iron and nickel are two of the materials used for making temporary magnets. |
(b) magnetic and non-magnetic materials.
| Magnetic materials | Non-magnetic materials |
| Materials that get attracted towards a magnet are called magnetic materials. | Materials that do not get attracted towards a magnet are called non magnetic materials. |
| Examples: Iron, Steel, cobalt, nickel etc. | Examples: Paper, wood, straws etc. |
2. Two bar magnets, ‘P’ and ‘Q’ are kept as shown in the following diagram.
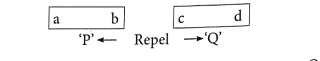
(a) If Point ‘c’ represents the south pole of the magnet Q, which point represents the north pole of magnet P?
(b) What will happen when the end ‘d’, of magnet ‘Q’ is brought towards the end ‘b’ of magnet ‘P’?
Answer 2(a): point ‘a’ represents the north pole of magnet P.
Answer 2(b): The magnets will start attracting each other when the end ‘d’, of magnet ‘Q’ is brought towards the end ‘b’ of magnet ‘P’.
3. Describe, in brief, the construction of a compass needle. State its main use.
Answer 3: The compass Consists of a magnetic needle pivoted at its centre and free to rotate a horizontal plane. The needle is fitted in a horizontal box having a glass cover. The compass also has a dial with a directions mark on it.
It is used to locate the north and south direction at a place.
4. Draw a labelled diagram to show the proper way of storing two bar magnets’, when they are not in use. State the advantage of such a ‘proper storing’.
Answer 4:
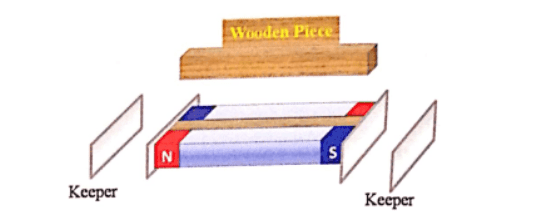
The advantage of proper storing of bar magnets is- Bar magnets do not lose their magnetism for a long period of time.
5. Write the different ways through which magnets can be made to lose their magnetism.
Answer 5:
The different ways through magnets can lose their power are as follows:
1) By throwing it from a high place
2) By heating it at a high temperature.
3) By hitting the magnets.
4) By not storing it properly their strength keeps on decreasing with time.
6. Anushtha saw a steel clip at the bottom of a very shallow puddle of water. She used a magnet, to take out this clip, without wetting her hands, or the magnet. Describe how she must have done this.
Answer 6: She must have used a strong magnet that can attract the steel clips located at the bottom of a very shallow puddle of water.
very very nice
Thanks Please Share this Website with your friends.