Are you looking for DAV Books Solutions then you are in right place, we have discussed the solution of Science class 8 book Chapter 16 Electric Current and Its Chemical Effects which is followed in all DAV School. Solutions are given below with proper Explanation please bookmark our website for further updates!! All the Best !!
DAV Class- 8 | Electric Current and Its Chemical Effects Question and Answer
Something To Know
A. Fill in the blanks:
1. Most liquids, that conduct electricity, are solutions of Acid, base and Salt.
2. The greater concentration of an ion in the solution, the greater is the conductivity of the solution.
3. The passage of an electric current, through a solution, can cause chemical effects.
4. When an electric current is passed through copper sulphate solution, copper gets deposited on the plate connected to the negative terminal of the battery.
5. The process, in which electricity is used to deposit a thin layer of any desired metal on another metallic object, is known as electroplating.
6. The faster is the relative motion between the magnet and the (closed) coil, the stronger is the current that flows through the coil.
B. State true or false for the following statements:
| 1. A solution of silver nitrate is a good electrolyte. | True |
| 2. An electrolytic cell consists of a cathode, anode and an electrolyte. | True |
| 3. Oxygen gets liberated at the anode during the electrolysis of acidified water. | True |
| 4. Electrorefining is the process of coating one metal on another using an electric current. | False |
| 5. The phenomenon of Electro-magnetic Induction’ was discovered by the Italian scientist, Alessandro Volta. | False |
C. Tick the correct Option:
1. The names of four electrolytes are given below: (A) Sea water (B) Tap water (C) Nitric acid (D) Oxalic acid Out of these, the weak electrolytes are the ones labelled as—’: A and B ❑B and D ❑ BandC ❑ A and D
Answer. B and D
2. Electrolytes conduct electricity due to the movement of—❑ The electrolyte itself ❑ Electrons only ❑ Positive as well as negative ions ❑ The electrodes themselves
Answer. Positive as well as negative ions
3. The electrode, connected to the positive terminal of a battery, is known as the—❑ Anode ❑ Positive pole ❑ Cathode ❑ Electrorefiner
Answer. Anode
4. The phenomenon of decomposition of an electrolyte, when electricity is passed through it, is known as—❑ Conduction ❑ Coating ❑ Electrolysis ❑ Electrorefining
Answer. Electrolysis
5. The process, of coating of (say) iron with chromium, is known as—❑ Extraction ❑ Electrolysis ❑ Electroplating ❑ Electrorefining
Answer. Electroplating
D. Answer the following questions in brief:
1. State the appropriate term, used for a liquid or solution, which can conduct electricity (along with some accompanying chemical changes).
Ans. Electrolyte
2. Distinguish between strong and weak electrolytes. Give two examples of each.
Ans. A strong electrolyte completely dissociates into its ions in a solution, while a weak electrolyte incompletely dissociates into its ions in a solution. Nitric acid and sulphuric acid are strong electrolytes. Tap water and oxalic acid are weak electrolytes.
3. Name the device that converts—(a) Chemical energy into electrical energy (b) Mechanical energy into electrical energy
Ans. (a) Cell, (b) Generator
4.Name the scientists who introduced the (scientific) world to the (a) Voltaic cell (b) Phenomenon of electrolysis (c) Phenomenon of electromagnetic induction
Ans. (a) Alessandro Volta, (b) Alessandro Volta, (c) Michael Faraday
5. An electrode ‘A’ is connected to the positive terminal while electrode B’ is connected to the negative terminal of a battery, as shown in the diagram.
(a) Give the names of the electrodes A and B. (b) Name the process associated with the circuit shown here. (c) Name the gases produced at A and B.
Ans. (a) A is anode and B is cathode (b) Electrolysis (c) Oxygen at A and Hydrogen at B
6. State the meaning of the terms: (a) Electromagnetic induction (b) Electrolysis (c) Electrodes (d) Electrorefining of metals
Ans. (a) Electromagnetic induction : The production of electricity by a changing magnetic field is called electromagnetic induction.
(b) Electrolysis : The chemical change in an ionic solution by passing an electric current is called electrolysis.
(c) Electrodes : A metal rod/plate through which electric current enters or leaves an electric cell is called an electrode.
d) Electrorefining of metals: Obtaining pure metal from impure metal by electrolysis is called electrorefining of metals.
7. State three uses of the phenomenon of electrolysis.
Ans. Following are the three uses of electrolysis: • Electrorefining of metals • Electroplating • Extraction of metals
1)it is used in industry in the formation of metals and non-metals. for example aluminium.
2)Electrolysis is commonly employed for coating one metal with another ie. Electroplating
3)it can also be used for the production of hydrogen and oxygen gases from water for extracting pure metals from metallic compounds.
E. Answer the Following Question
1. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Solid chloride does not conduct electricity while sodium chloride solution conducts.
Answer: Solid sodium chloride does not provide free ions, while its solution provides free ions. Hence, solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity while its solution conducts electricity.
(b) It is not safe to carry out electrical repairs outdoors during a heavy downpour.
Answer: Rainwater often contains many dissolved salts in it. So, rainwater is a good conductor of electricity. Hence, carrying out electric repairs during a heavy downpour poses the risk of electric shock. So, it is not safe to carry out electric repairs during a heavy downpour.
(c) To carry out electrolysis of water, a few drops of sulphuric acid are (carefully) added to the water.
Answer: Adding a few drops of sulphuric acid makes the water more conducting. So, a few drops of sulphuric acid are carefully added to water while carrying out electrolysis of water.
(d) Kitchen gas burners are often coated with chromium.
Answer: The coat of chromium prevents corrosion of the gas burner. Hence, kitchen gas burners are often coated with chromium.
2. Three electrolytic cells A, B and C are connected with identical bulbs in separate circuits as shown in the diagram. Electrolytic cell A contains sodium chloride solution and Electrolytic cell B contains acetic acid solution. The electrolytic cell C contains distilled water.
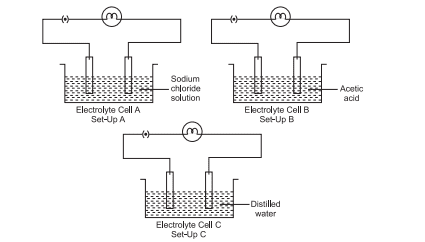
(a) In which Set-up will the bulb glow the brightest? Justify your answers.
Answer: In Set-up A, because sodium chloride is a strong electrolyte.
(b) In which Set-up will the glow of the bulb be quite dim? Justify your answers.
Answer: In Set-up B, because acetic acid is a weak electrolyte.
(c) In which Set-up will the bulb not glow at all? Justify your answers.
Answer: In Set-up C, because distilled water is a bad conductor of electricity.
3. Ramit sets-up the circuit shown below for purification of copper:

(a) Name the metals used for Electrodes A and B.
Answer: Impure copper for electrode A and pure copper for electrode B.
(b) Name the process of purification.
Answer: Electrorefining
(c) Name the solution that needs to be used.
Answer: Copper sulphate
4. (a) Define ‘electroplating’. How can steel spoons be plated with silver? Explain with the help of a diagram.
Answer: The process of depositing a thin layer of some desired metal, over some other metallic object, with the help of an electric current is called electroplating.
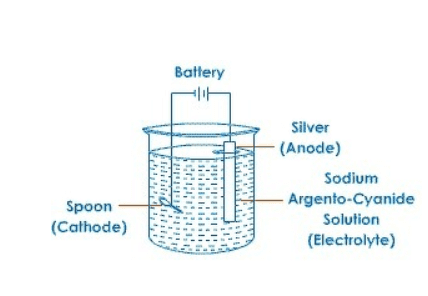
For this, a plate of pure silver is made the anode, while the steel spoon is made the cathode. When electric current flows through the set-up, pure silver from anode dissociates and gets deposited on cathode. Thus, a coat of silver is applied on the spoon.
(b) State any three uses of electroplating.
Answer: Three uses of electroplating are:
- It makes the surfaces shiny.
- It makes the surfaces durable.
- It prevents corrosion.
5. Describe an experiment to show that we can get electrical energy by using a magnet.
Answer: Take a hollow cylindrical pipe of iron and wind a large number of turns of well-insulated copper wire on it. Clean the two ends of the wire and attach a torch bulb/LED to it. Now, take a strong bar magnet and move it rapidly towards the centre of the pipe (without touching it). We find that the bulb glows. However, it glows only for a while and stops glowing as soon as the magnet is stopped. If we now withdraw the magnet away from the coil, we find that the bulb again glows up’ momentarily. We are, thus, getting electricity through this motion of the magnet near/through a coil.
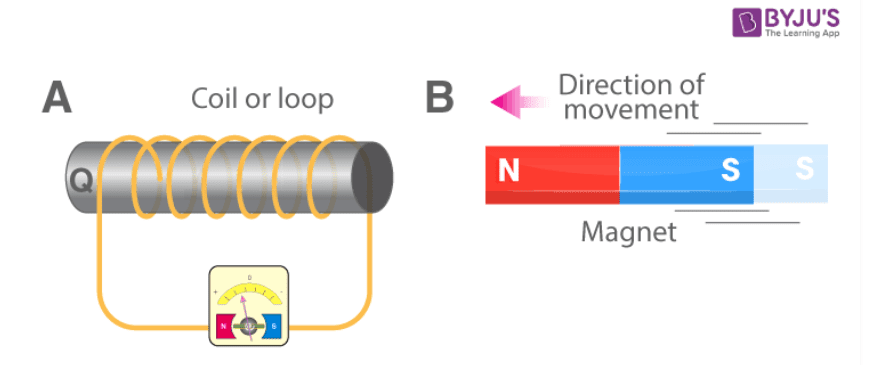
6. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a torch bulb. State the likely response of the bulb, if a bar magnet is-
(a) pushed into the coil?
Answer: Bulb glows.
(b) pulled out of the coil?
Answer: Bulb glows.
(c) held stationery within the coil?
Answer: Bulb does not glow.
Something To Do
Do it yourself
Other Related Chapters
- Chapter 1 | The Cell – Its Structure and Functions | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 2 | Microorganisms: Friends or Foes | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 3| Metals and Non-Metals| Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 4| Force and Pressure | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 5| Friction | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 6| Sources of Energy | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 7| Combustion | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 8| Conservation of Plants and Animals | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 9| Crop Production and Its Management | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 10| Refraction and Dispersion of Light | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 11| The Human Eye | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 12| Sound | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 13| Synthetic Fibres and Plastics | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 14| Reproduction in Animals | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 15| Reaching the Age of Adolescence | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 16| Electric Current and Its Chemical Effects | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 17| Stars and Solar System | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 18| Earthquakes | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 19 | Pollution of Air | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 20 | Pollution of Water | Class- 8 DAV Science
Thanks
Thanks friend
Please send part d I want it