India DAV Class 6 SST Chapter 6 Question Answer My Motherland delves into the exercises from the textbook “We and Our World Book.” The India’s DAV Class 6 SST Solutions The My Motherland exercises at the end of Chapter 6 will be useful for school exams.
Dav Class 6 SST Chapter 6 Geography India My Motherland Solutions
A. Tick the correct option.
1. The southernmost tip of the mainland of India is-
Ans: Kanyakumari
2. Which of the following is the largest glacier in India?
Ans: Siachin
3. Which is the highest range of the Himalayas?
Ans: Himadri
4. The Thar desert lies to the west of-
Ans: Aravalli hills
5. Which River flows westwards into the Arabian sea?
Ans: Narmada
B. Fill in the blanks.
1. The area lying in the north of Tropic of Cancer is called Sub-tropical India
2. An ocean named after India is the Indian Ocean
3. Indira Point is located at Southernmost latitude.
4. K2 is the second-highest peak of the world and lies in Karakoram range.
5. River Satluj is the major tributary of Indus River.
C. Match the following:
Answer: (1) d, (2) a, (3) b, (4) e, (5) c.
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
1. What is the area and size of India in respect to the world?
Ans: India is a vast country with an area of 3.28 million square kilometres. India is the seventh largest country in the world.
2. Which countries form Indian sub-continent? Why is it called so?
Ans: India along with its neighbors Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh form a distinct geographical unit popularly known as Indian sub-continent.
3. What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India?
Ans: The latitudinal extent of India is between 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N. The longitudinal extent is between 68°7′ E and 97°25′ E.
4. Name the three major rivers which form the Great Northern Plains of India.
Ans: The three major rivers which form the Great Northern Plains of India are Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra.
5. Name the newly formed 29th state of India. When was it formed?
Ans: Telangana is the newly formed 29th state of India. It was formed on 2nd June of 2014.
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
1. What is the area and size of India in respect to the world?
Ans: India is a vast country with an area of 3.28 million square kilometres. India is the seventh largest country in the world.
2. Which countries form Indian sub-continent? Why is it called so?
Ans: India along with its neighbors Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh form a distinct geographical unit popularly known as Indian sub-continent.
3. What is the latitudinal and longitudinal extent of India?
Ans: The latitudinal extent of India is between 8°4′ N and 37°6′ N. The longitudinal extent is between 68°7′ E and 97°25′ E.
4. Name the three major rivers which form the Great Northern Plains of India.
Ans: The three major rivers which form the Great Northern Plains of India are Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra.
5. Name the newly formed 29th state of India. When was it formed?
Ans: Telangana is the newly formed 29th state of India. It was formed on 2nd June of 2014.
E. Answer the following questions.
1. State any four main features of the Himalayan mountains.
Ans: The four main features of the Himalayan mountains are:
- The Himalayan mountains are the youngest mountains in the world. They are folded mountains.
- They run along the northern border of India and form an arc which is around 2,400 km long.
- It has world’s highest peak.
- It is famous for hill stations like Shimla, Mussoorie, Nainital, Darjeeling, etc.
2. Where is the Sundarban delta? How is it formed? What makes it special in the world?
Ans: The Sundarban Delta is located on the Bay of Bengal. It is formed by the confluence of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers. It is famous for Royal Bengal tigers and mangroves trees. It is the largest delta which makes it special in the world.
3. Describe the Peninsular plateau of India.
Ans: Peninsular plateau is a tableland and is composed of the old crystalline, igneous and metamorphic rocks. It was formed due to the breaking and drifting of the Gondwana land. It has broad and shallow valleys and rounded hills. It consists of two broad divisions-Central the highlands and Deccan Plateau. The eastward extensions of this plateau are locally known as the Bundelkhand and Baghelkhand.
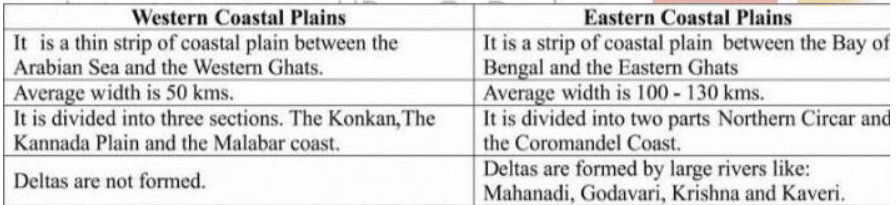
4. How do the Eastern coastal plains differ from the Western coastal plains?
Ans: The Eastern coastal plains differ from the Western coastal plains in following ways:
5. Distinguish between Andaman and Nicobar Islands and the Lakshadweep Islands.
Ans:
