What is Mineral ?
A naturally occurring substance that has a definite chemical composition is a mineral. Minerals are not evenly distributed over space. They are concentrated in a particular area or rock formations. Some minerals are found in areas which are not easily accessible such as the Arctic ocean bed and Antarctica. Minerals are formed in different types of geological environments, under varying conditions. They are created by natural processes without any human interference. They can be identified on the basis of their physical properties such as colour, density, hardness and chemical property such as solubility.
Types of Minerals
There are over three thousand different minerals. On the basis of composition, minerals are classified mainly as metallic and non-metallic minerals.
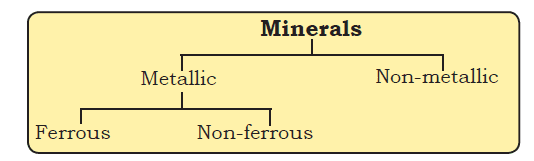
Metallic minerals contain metal in raw form. Metals are hard substances that conduct heat and electricity and have a characteristic lustre or shine. Iron ore, bauxite,
manganese ore are some examples. Metallic minerals may be fer rous or non-ferrous. Ferrous minerals like iron ore, manganese and chromites contain iron. A
non-ferrous mineral does not contain iron but may contain some other metal such as gold, silver, copper or lead.
Non-metallic minerals do not contain metals.
Limestone, mica and gypsum are examples of such minerals. The mineral fuels like coal and petroleum are also non-metallic minerals.
Minerals can be extracted by mining, drilling or quarrying
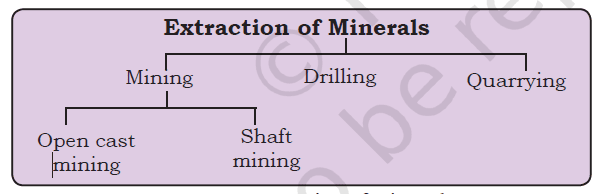
The process of taking out minerals from rocks buried under the earth’s surface is called mining. Minerals that lie at shallow depths are taken out by removing the surface layer; this is known as open-cast mining. Deep bores, called shafts, have to be made to reach mineral deposits that lie at great depths. This is called shaft mining. Petroleum and natural gas occur far below the earth’s surface. Deep wells are bored to take them out, this is called drilling. Minerals that lie near the surface are simply dug out, by the process known as quarrying.
Distribution in minerals in India
Iron: India has deposits of high grade iron ore. The mineral is found mainly in Jharkhand, Odisha,
Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Goa, Maharashtra and Karnataka.
Bauxite: Major bauxite producing areas are Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat,
Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
Mica: Mica deposits mainly occur in Jharkhand, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh and Rajasthan. India is the largest producer and exporter of mica in the world.
Copper: It is mainly produced in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Manganese: India’s manganese deposits lie in Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.
Limestone: Major limestone producing states in India are Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
Gold: Kolar in Karnataka has deposits of gold in India. These mines are among the deepest in the world which makes mining of this ore a very expensive process.
Salt: It is obtained from seas, lakes and rocks India is one of the world’s leading producers and exporters of salt.