Vegetative propagation is a type of reproduction found in higher plants in which a new plant is formed from a vegetative part of the plant such as roots, stems or leaves for eg. in potato, bryophyllum, sweet potato etc. Vegetative propagation occurs through leaf in Bryophyllum.
Natural vegetative propagation
Some of the common modes of natural vegetative propagation are as follows:
- Roots – Tubers (modified roots) help in the development of new plants. Every bud is created at the stem’s base. Dahlia is a quick example.
- Stem – Buds form at the nodes of runners that grow up the ground level. The buds grow into a completely new species. Mint grows by this process.
- Leaves – The leaf of a plant will detach, fall off and start growing again as a separate plant. One of the best examples for leave propagation is that of Bryophyllum.
- Bulbs – Leaves are connected to the underground stem from the bulbs to store plant food. A shoot is then developed from the buds of the plant called the lateral buds. Garlic and onion grow this way.
Artificial Vegetative Propagation
Artificial Vegetative Propagation and its types:
(A) Cutting
(B) Layering
(C) Grafting
(A) Cutting : This is the very common method of vegetative propagation practiced by the gardeners. It is the process in which a vegetative portion from plant is taken and is rooted in the soil to form a new plant. e.g. Grapes, Sugarcane etc.
(B) Layering : In this process the development of adventitious roots is induced on a stem before it Parent plant e.g Mango, roses etc.
It is of two types :
- Mound Layering
- Air Layering
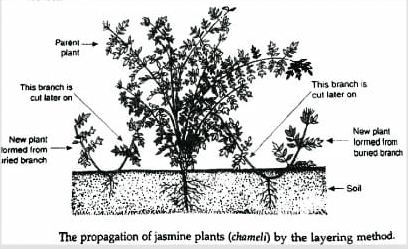
(i) Mound Layering : In this process of layering the lower stem branch of plant is used.
Leaves are removed from this stem. Then it is bent close to the ground, pegged and covered with the moist soil in such a way that it’s growing tip remains above the soil surface. This pegged down branch is called as layer. After a few days the covered portion of stem develops roots. This stem is then detached from the parent plant and is grown separately into a new individual. e.g. Jasmine
(ii) Air layering : It is adopted in those plants where stem cannot be bent to the ground. In this process the stem is girdled (i.e. ring of the bark is removed).
Then it is covered with moist moss or cotton and wrapped with a polythene sheet to preserve the moisture. After few weeks adventitious roots develop from the injured part. The branch along with roots is then separated from the parent plant and planted to grow into a new plant. e.g. Orange, Pomegranate etc.
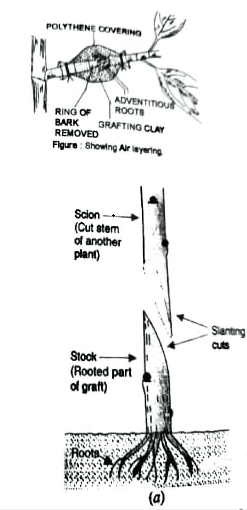
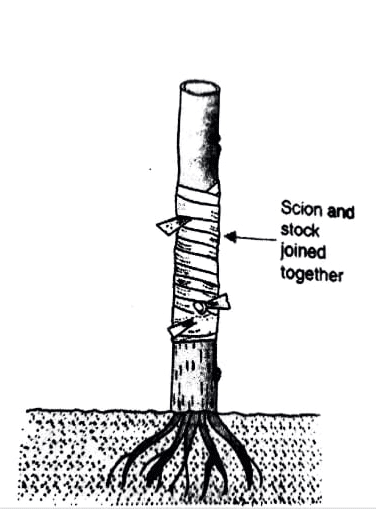
(C) Grafting : The process of joining together of two different plants in such a manner that they live as one plants is called as grafting. Out of the two plants one is rooted in the soil and is known as the stock. The other part consists of a small shoot bearing one or more buds ,it is known as scion.
Their union is carried out in such a way that their cambium must overlap each other. e.g. Mango, roses etc.
Significance of vegetative propagation
(A) It is used to propagate a plant in which viable seeds are not formed or very few seeds are produced, e.g. Orange, pineapple, banana etc.
(B) Vegetative propagation helps us to introduce plants in new areas where the seed germination fails to produce mature plant due to change in environmental factors and the soil.
(C) Vegetative propagation is a more rapid, easier and cheaper method of multiplication of plants.
(D) By this method a good quality of a race or variety can be preserved.
(E) Most of the ornamental plants are propagated through vegetative propagation. e.g. Rose, Tulip etc.
Common Frequently Asked Questions
Vegetative propagation : This is a type of reproduction found in higher plants in which a new plant is formed from a vegetative part of the plant such as roots, stems or leaves for eg. in potato, bryophyllum, sweet potato etc.
(A) It is used to propagate a plant in which viable seeds are not formed or very few seeds are produced, e.g. Orange, pineapple, banana etc.
(B) Vegetative propagation helps us to introduce plants in new areas where the seed germination fails to produce mature plant due to change in environmental factors and the soil.
(C) Vegetative propagation is a more rapid, easier and cheaper method of multiplication of plants.
(D) By this method a good quality of a race or variety can be preserved.
(E) Most of the ornamental plants are propagated through vegetative propagation. e.g. Rose, Tulip etc.
Advantages of vegetative propagation
- Quicker and more certain and cheaper in price.
- Produces identical quality as the parent.
- Plants that do not have viable seed, can be reproduced.
- Flowers produced are of superior quality.
- Desirable character of fruit can be maintained.
Disadvantages of vegetative reproduction
- Does not produce new variety.
- Leads to overcrowding around the parent plant.
- Very little possibility of dispersal.
Radish
Potato
Bryophyllum part which is used for vegetative propagation is leaf.
Flowers of the plant is not involved or used in Vegetative Propagation.
Cutting, Layering and grafting are artificial method of vegetative propagation.
Grafting is the process of joining together of two different plants in such a manner that they live as one plants. Out of the two plants one is rooted in the soil and is known as the stock.
Vegetative propagation takes place in potato by Stem.
Stem layering is the method of vegetative reproduction used in jasmine plants.
Artificial Vegetative Propagation and Natural vegetative propagation are two methods of vegetative reproduction. Natural Methods of vegetative reproductions are through roots, stems ,leaves and bulbs while Artificial vegetative propagation is done through cutting ,layering and grafting.
Potato, bryophyllum, sweet potato are some plants which shows vegetative propagation.
Grootee
The stem cutting from the donor plant is called Scion
Also Visit: