Are you looking for DAV Books Solutions then you are in right place, we have discussed the solution of Science class 8 book Chapter 14 Reproduction in Animals which is followed in all DAV School. Solutions are given below with proper Explanation please bookmark our website for further updates!! All the Best !!
DAV Class- 8 Reproduction in Animals Question and Answer
Something To Know
A. Fill in the blanks:
1. Genetically identical individuals are produced by asexual reproduction.
2. Gametes are the specialised cells that take part in sexual reproduction.
3. An animal, that produces both male and female gametes, is known as a hermaphrodite animal.
4. A fertilised egg is also known as the Zygote.
5. The incubation period for a hen’s egg is 21 days.
B. State true or false for the following statements:
Ans:
| Column I | Column II |
| 1.Hydra | (c) Budding |
| 2.Reptiles | (d) Oviparous |
| 3.Earthworm | (a)Hermaphrodite |
| 4.Gills | (e)Tadpole |
| 5. Egg Shell | (b) Calcite |
C. Tick the correct Option:
1.The Site of fertilization , in human, is the –
Ans: Oviduct
2. The reason why parrot does not belong to the same group as that of monkey, man, cat is that-
Ans: It is Oviparous
3.An organism which reproduces by Budding is-
Ans: Yeast
4. A caterpillar develops into a silk moth through the process of
Ans: Metamorphosis
5. A foetus can be best defined as-
Ans: A well developed embryo
D. Answer the following questions in brief:
1.Distinguish between asexual and sexual production.
Ans:
| Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
| A single parent is involved. | Two parents are involved. |
| Gametes are not formed. | Gametes are formed. |
| It is a fast process. | It is slow process. |
2.How is reproduction carried out in Hydra?
Ans: Reproduction in Hydra is caused by Budding.
3. How is fertilization in a hen different from fertilization in a frog?
Ans: Internal fertilization takes place in a hen, while external fertilization takes place in a frog.
4.State the difference between oviparous and viviparous animals.
Ans: Oviparous animal lay eggs while viviparous animal give birth to young ones.
5.Why is the number of eggs, laid by frogs at a time, much higher than those laid by a hen?
Ans. A frog lays eggs in water, where eggs are exposed to predators and water current. But a hen lays eggs on land and takes care of them during incubation. Most of the eggs of a frog are destroyed by the time tadpoles come out of some of them. Hence, a frog needs to lay thousands of eggs. This is not the case with a hen.
6. How will you differentiate between a zygote and an embryo?
Ans. A zygote is unicellular, while an embryo is multicellular.
7.It is the mother who gives birth to a child. How do children, then, get features of both the parents?
Ans. A child gets genes from its father and mother. Hence, a child gets features from both the parents.
E. Value-Based Questions
1. Define the term ‘Metamorphosis’. List the changes that a tadpole undergoes to develop into a frog.
Ans:Metamorphosis is a process by which an organism gradually changes into a completely different one. For eg; a butterfly is developed from a larva through metamorphosis in a period of time.
The changes that a tadpole undergoes to develop into a frog are:
1. Eggs
2. Embryo
3. External gills develop for breathing.
4. The tadpole’s tail keeps growing.
5. It’s hindlegs develop.
6. Front legs appear.
7. Tail becomes shorter.
8. It changes into ‘young frog’ or ‘froglet’.
9. It finally becomes an adult frog.
2. Trace the sequence of events that lead to development of a chick from the fertilised egg of a hen.
Ans: After fertilisation, the zygote starts dividing and moves down the oviduct. As it moves down, a number of protective layers get formed around it. The egg shell is one of these protective layers. The embryo develops inside the egg for around 21 days. Finally the egg shell breaks down and the chick comes out.
3. Where does fertilisation occur in human beings? How does the zygote formed eventually develop into an infant?
Ans: Fertilisation occurs in oviduct in human female reproductive system. The zygote immediately divides into two cells. Then these cells divide again and again over the couple of days. This results in formation of a cluster of cells. This cluster of cells is called embryo. It moves down to the uterus and gets implanted in the lining of the uterus. It undergoes further rounds of cell divisions. Gradually, the embryo develops into the foetus. A foetus resembles a human being. After about 40 weeks of gestation, the fully developed child is ready to take birth.
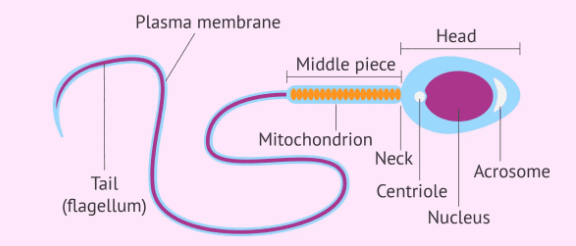
4. Draw a neat well-labelled diagram of the human sperm. Also, write how its shape and size help it in its functioning?
Answer: A sperm is smaller in size than the ovum and can only be seen through a microscope. Each sperm cell has three parts: a head, a middle piece and a tail. A structure, at the tip of the head, produces enzymes that help the sperm to penetrate the female ovum.
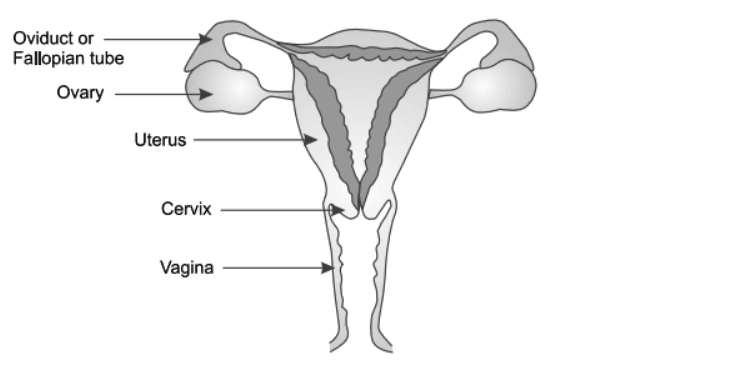
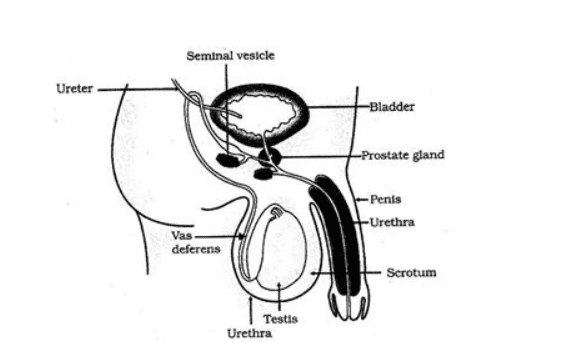
5. Draw a neat and well labelled diagram of (i) the reproductive system of the human female (ii) the male reproductive system.
Answer:
(1) diagram of the reproductive system of the human female
(2) diagram of the male reproductive system.
6. Write the function(s) of each of the following parts of the human female reproductive system:
(a) Ovaries
Answer: Ovaries produces egg.
(b) Oviduct
Answer: Oviduct is the site of fertilisation.
(c) Uterus
Answer: Uterus is the site of implantation and further development of embryo.
Something To Do
Do it yourself
Other Related Chapters
- Chapter 1 | The Cell – Its Structure and Functions | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 2 | Microorganisms: Friends or Foes | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 3| Metals and Non-Metals| Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 4| Force and Pressure | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 5| Friction | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 6| Sources of Energy | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 7| Combustion | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 8| Conservation of Plants and Animals | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 9| Crop Production and Its Management | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 10| Refraction and Dispersion of Light | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 11| The Human Eye | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 12| Sound | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 13| Synthetic Fibres and Plastics | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 14| Reproduction in Animals | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 15| Reaching the Age of Adolescence | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 16| Electric Current and Its Chemical Effects | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 17| Stars and Solar System | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 18| Earthquakes | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 19 | Pollution of Air | Class- 8 DAV Science
- Chapter 20 | Pollution of Water | Class- 8 DAV Science
plzz upload fast it would be helpful
uploaded please check here