Are you looking for DAV Books Solutions then you are in right place, we have discussed the solution of Science class 7 book Chapter 2 Nutrition in Living Organisms -Animals which is followed in all DAV School. Solutions are given below with proper Explanation please bookmark our website for further updates!! All the Best !!
DAV Class- 7 Nutrition in Living Organisms Animals Question and Answer
Something To Know
A. Fill in the blanks.
1. The digestion of food in humans starts in the Mouth and is completed in the Small intestine.
2. Hydrochloric acid present in the stomach, kills bacteria.
3. The largest gland in the human body is the liver.
4. Partially digested food, that is chewed again by grass eating animals, is called the Cud.
5. Amoeba uses pseudopodia for locomotion and for capturing its food.
B. Match the following:
Ans:
| Column I | Column II (Answer) |
| Gall bladder | (a) Bile Juice |
| Proteins | (e) Amino acids |
| Intestinal wall | (c) Absorption |
| Rumen | (b) Cow |
| Pseudopodia | (d) False feet |
C. Tick the correct option.
1. Organism that can synthesize their own food is called
Ans 1: Autotrophs
2. Cow is a/an
Ans 2: Heterotroph
3. Animals that eat both plants and materials are called
Ans 3: Omnivores
4. Which one of these is not part of the alimentary canal.
Ans 4: liver
5. Bile Juice is released by
Ans 5: liver
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
1. Define the following terms:
(a) Holozoic nutrition
Answer 1(a): Holozoic nutrition is the mode of nutrition in which organisms, like Amoeba and Human Beings, eat food that might be in a solid or liquid state. Amoeba follows holozoic nutrition.
(b) Alimentary canal
Answer 1(b): The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular organ that starts at the mouth and terminates at the anus and is responsible for the digestion and absorption of the ingested food and liquids.
2. Give the meaning of the terms:
(a) Assimilation
Answer 2(a): The absorbed food is utilized by the body for the growth and formation of body parts. This process is known as assimilation.
(b) Rumination
Answer 2(b): The process of chewing cud thoroughly is called rumination.
3. Name the organs that make up the human alimentary canal.
Answer 3: The organs that make up the human alimentary canal are:
(1) Mouth and Buccal cavity (2) Food pipe (or Oesophagus) (3) Stomach (4) Small intestine (5) Large intestine (6) Anus.
4. State two differences between milk teeth and permanent teeth.
Answer 4: Two differences between milk teeth and permanent teeth are: –
Milk teeth
(1) They start appearing, above the gumline, when a baby is six, or seven months old.
(2) They are 20 in numbers.
Permanent teeth
(1) They start appearing when a child is around the age of 6 years.
(2) They are 32 in numbers.
5. Name the four types of teeth in the human mouth.
Answer 5: The four types of teeth found in the human mouth are:
(1) Incisors (2) Canines (3) Premolars (4) Molars
6. State the function of the (a) incisor teeth (b) premolar teeth.
Answer 6: (a) Incisors are used for cutting the food.
(b) Premolars are used for grinding the food.
7. State the role of acid in the human stomach.
Answer 7: The role of acid in the human stomach is to kill the bacteria and also provide the acidic medium, needed for the digestion of food by the enzymes in the stomach.
8. State the function of (a) bile juice and (b) pancreatic juice in the human digestive system.
Answer 8: (a) The bile juice plays an important role in digestion of fats.
(b) The pancreatic juice acts on carbohydrates, proteins and fats and breaks them into simpler forms.
E. Answer the following questions.
1. Draw a neat, well labelled diagram of the human digestive system.
Answer 1.
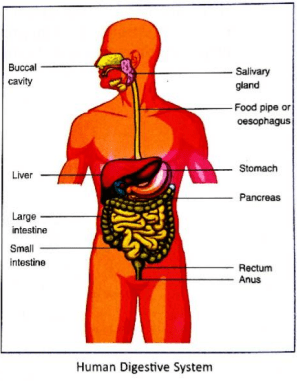
2. Justify the following statements:
(a) Crow is an omnivore.
Answer 2(a): Crow is an omnivore because it feeds on both plants and animal materials.
(b) It is said that the mode of nutrition, in human beings and Amoeba, is quite similar.
Answer 2(b): Yes, Nutrition in human beings and Amoeba is quite similar i.e., holozoic mode of nutrition. They eat food that may be in solid or in liquid form.
3. Give reasons for the following:
(a) Ingestion of food is difficult without teeth.
Answer 3(a): Ingestion of food is difficult without teeth because it breaks down the food into smaller pieces that are easy to swallow.
(b) If we chew rice, or bread, for a few minutes, it starts tasting sweet.
Answer3(b): If we chew rice, or bread, for a few minutes, it starts tasting sweet because saliva present in our mouth break down starch into sugar.
(c) Bacteria are present in the caecum of ruminants.
Answer 3(c): Bacteria present in the caecum help in the digestion of the cellulose of the food.
4. Explain how digested food gets absorbed into the blood.
Answer 4: The inner wall, of the small intestine, absorbs the digested food. It has a large number of finger-like projections, called villi. The villi increase the effective surface area for absorption of digested food. This absorbed food is passed to blood vessels, present in the villi.
5. State, in one/two sentence/s each, the various processes involved in nutrition in ruminant animals.
Answer 5: The various processes involved in nutrition in ruminant animals are:
(1) The animals first swallow the food quickly and store it in their rumen. The rumen has some micro-organisms that help in partial digestion of the cellulose of the plant materials. This food is now called cud.
(2) The ruminants, later on, bring this cud back to their mouth and chew it thoroughly. This process is called rumination.
(3) The thorough chewing of food during rumination, helps to break down the rich cellulose content of the plant materials.
(4) Ruminants also have a spacious bag-like structure, between their small intestine and the large intestine. This is called the caecum. The bacteria, present in the caecum, help in further digestion of the cellulose of the food.
6. Explain ingestion of food, in amoeba, through a diagram.
Answer 6: When Amoeba comes in contact with food, it produces pseudopodia around the food particle. As the cell membranes of the pseudopodia fuse, the food gets trapped in a food vacuole. Digestive juices are secreted into this vacuole to digest the food.
1 thought on “Chapter 2 | Nutrition in Living Organisms-Animals | Class- 7 DAV Science Solutions”