DAV CLASS 8 Social Science Solutions: Students who are looking for DAV Social Science Books Solutions then you are in right place, we have discussed the solution of Social Science class 8 book chapter 22 Safeguarding the Marginalised followed in all DAV Schools. Solutions are given below with proper Explanation please bookmark our website for further updates!
DAV CLASS 8 Safeguarding the Marginalised Social Science Question and Answers
Something to do.
A. Tick (✓) the correct option.
1. Manual Scavenging has been declared illegal as it violates—
Ans 1. (c) Right against Exploitation
2. When was Swachh Bharat Mission launched?
Ans 2. (d) October 2, 2014
3. Which out of the following is true about the Directive Principles of State Policy?
Ans 3. (a) They are not enforceable by law.
4. Which one of the following Fundamental Rights has special provisions for the minorities?
Ans 4. (b) Culture and Educational Rights
5. Identify the scheme under which a person can open a bank account without depositing any money.
Ans 5. (b) PMJDY
B. Fill in the blanks.
1. Untouchability is an inhuman product of the caste system.
2. PMAY (Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana) is a welfare housing scheme launched by the Central Government.
3. The important challenges we face today are the unevenness of our growth processes and the inequalities that remain in our social institutions.
4. PMSBY (Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana) is an initiative to provide insurance benefits to the rural population.
5. Manual scavenging violates the Fundamental Right against exploitation and discrimination.
C. Write True and False for the following statements.
1. The State cannot make special provisions for the backward classes.
2. The practice of untouchability has been abolished under the Right to Equality.
3. Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana provides financial empowerment to the girl child.
4. Minorities in India are not protected by the Constitution.
5. The Directive Principles of State Policy promote the welfare of the people.
Ans. 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True
D. Answer the following questions in brief.
1. What is meant by marginalisation? Who are the marginalised groups in India?
Ans 1. Marginalisation means the social process of discriminating and isolating an individual or a group to a lower or an outer edge and treating them as ‘inferiors’. In most cases, the deprivation leads to impoverishment and unemployment. The marginalized groups refer to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Class,es and many minority groups who suffer from backwardness.
2. Explain the meaning of Protective Discrimination? How does it ensure socio-economic justice to the deprived section of society?
Ans 2. Protective Discrimination means that the State can make special provisions to protect the interest of the socially and economically backward classes. The government can implement special schemes and measures so that they can get opportunity to occupy better socio-economic positions, at par with the persons of other castes and forge new social relations with others, irrespective of caste consideration.
3. Explain the main provisions of the Cultural and Educational Rights.
Ans 3. Cultural and Educational Rights: The Constitution has provisions that safeguard the Cultural and Educational Rights of minorities. Minorities are free to practice their cultural aspects like festivals and other rituals. They can also run their own educational institutions for the betterment of their community members.
4. Which three Constitutional Provisions of the Indian Constitution safeguard the marginalized in India?
Ans 4. (1) Right to Equality
(2) Right against Exploitation
(3) Right to Freedom of Religion and Cultural and Educational Rights.
5. How do Directive Principles of State Policy promote the welfare of all sections of society? Give any three examples.
Ans 5. The Directive Principles of State Policy lay down major fundamentals in the governance of the country. (i) They direct the states to apply these principles while making laws to secure a social order for the promotion of the welfare of the people. (ii) They aim to minimize the inequalities in income and eliminate inequalities of status. (iii) They ensure that the material resources of the country are utilized for the common good.
E. Answer the following questions.
1. Describe any five welfare schemes launched by the Government of India for the upliftment of the needy and the downtrodden.
Ans 1. Five welfare schemes launched by the Government of India are as follows:
(i) Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY): It is primarily a welfare housing scheme launched by the Central Government. The houses would be distributed to the needy sections of society and a subsidy on loan would be provided by the Central Government, thereby making affordable housing for the economically weaker sections of the country. Special preference would be given to senior citizens, women, and SCs/STs in the allotment of these houses.
(ii) Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY): Under the PMJDY, any individual above the age of 10 years and does not have a bank account can open a bank account without depositing any money. The scheme targeted the people living Below Poverty Line (BPL) but is beneficial to everyone, who does not have a bank account.
(iii) Stand-Up India Scheme: The scheme aims to promote entrepreneurship among SCs/STs and women. It provides a composite loan for setting up any new enterprise between 10 lakh rupees and up to one crore.
(iv) Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Yojana (PMGKY): Under this Income Declaration scheme, the government would mobilize the money for utilising and meeting the welfare needs of the poor population.
(v) Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY): It lays special emphasis on the financial empowerment of the girl child. Through this scheme, the parents of any girl child below 10 years can open a saving account for their daughter and operate it till she attains the age of 21 years. After that time, they can withdraw the money and use it for their marriage or higher education. The scheme offers a high rate of return even much higher than PPF (Public Provident Fund).
2. What does the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan aim at? How far has it been successful so far? List any five tasks related to cleanliness which the students must undertake.
Ans 2. Swachh Bharat Abhiyan aims to achieve the following:
1. To construct toilets.
2. To eradicate manual scavenging.
3. To change people’s attitudes to sanitation and create awareness.
Swachh Bharat Mission can only be made successful if manual scavenging in the states is completely eliminated and replaced with modern toilets. The progressive rehabilitation of those dependent on scavenging has to be planned simultaneously through skill development programs so that they get suitably rehabilitated. Moreover, Swachh Bharat Mission will succeed only when each and every Indian become responsible for creating, managing waste, and not littering public places. Students must undertake the following tasks:
(i) Avoid littering in public places.
(ii) Keep their schools and homes clean.
(iii) Throw garbage in proper places.
(iv) Avoid throwing rubbish into rivers.
(v) Promote campaign to end open defecation.
3. Highlight any five special measures taken by the Government of India for the upliftment of Backward Classes.
Ans 3. The Government of India has taken several special measures for the upliftment of backward classes:
(i) The practice of untouchability has been abolished under the Right to Equality.
(ii) There are special provisions like Protective Discrimination. It means that the state can make special provisions to protect the interest of the socially and economically backward classes.
(iii) The government can implement special schemes and measures so that they can get opportunity to occupy better socio-economic positions at par with the persons of other castes and forge new social relations with others, irrespective of caste consideration.
(iv) The Directive Principles of State Policy lay down important fundamentals in the governance of the country. They direct the states to apply these principles while making laws to secure a social order for the promotion of the welfare of the people. They aim to minimise the inequalities in income and eliminate inequalities of status.
(v) The reservation policy of the Government of India is one of the special measures to provide social justice to all and to end inequalities in our society. Under this policy, seats are reserved for SC/ST/OBC in the legislatures, government services, schools, colleges, etc.
4. Explain the main provisions of Prevention of Atrocities Act 1989 for the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes. List any six offences which are punishable under this Act.
Ans 4. This Act prevents offences of atrocities against the members of SC/ ST. It contains a long list of offences and seeks to punish the offenders if proved guilty:
(i) Forcing a member of SC/ST to drink or eat any inedible or obnoxious substance.
(ii) Insulting or annoying any member of a SC/ST. (iii) Wrongfully dispossessing a member of a SC/ST from his land. (iv Compelling to do ‘begar’ or bonded labour.
(iv) Force anyone not to vote or to vote for a particular candidate.
(v) Use of force on any woman belonging to a SC/ST.
(vi) Committing the mischief by fire.
(vii) Causing destruction of a building that is ordinarily used as a place of worship or human dwelling.
5. How can we ensure that the marginalised and weaker section of society equally benefited from the Government programmes? Suggest any five measures.
Ans 5. (i) The marginalised and weaker section of society should be given enough opportunities to join the mainstream of the country. This can be possible only if their health and education are given top priority.
(ii) We must ensure that the interests of Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Backward Classes, Minorities, women and children are protected and justice is provided to them.
(iii) The abolition of untouchability by the Constitution means that no one can henceforth prevent Dalits from educating themselves, entering temples, using public facilities, etc. This should be made effective so that they really enjoy the benefits.
(iv) The Government of India should make all efforts to eradicate poverty, ignorance and disease which are deeply rooted in our societies, especially among the marginalised and weaker sections of society.
(v) Employment opportunities should be increased for them in order to empower them in the real sense.
Value Based Question
1.Manual scavengers have to remove human excreta from several homes every day. The government declaration of 100% Individual Household Latrine Coverage in the States differs from the ground reality. The fact remains that employing scavengers and constructing dry latrines continue in many parts of India inspite of the fact that this offence invites imprisonment up to one year and a fine of Rs. 2000. Study carefully the above given paragraph and answer the following questions: 1. What stringent measures can be taken to implement the law?
Ans 1. Some of the stringent measures:
(i) The government should prohibit the practice of open defecation and manual scavenging. The Supreme Court should order the Central and State government to verify the fact and take necessary steps against those who violate this law.
(ii) Education is the key to enlightenment and hence not only should the Dalits be educated but the upper caste mindset should also be encouraged to change these things and to stop manual scavenging and dry latrines construction.
2. In your opinion, should the manual scavengers be allowed to continue to earn their livelihood or banned? Justify your answer with three suitable arguments.
Ans 2. Manual scavenging should be banned as it is disgraceful practice. Manual scavengers are often given orders and that too in a very harsh and ruthless tone. They are neither paid well nor fed well, but they are helpless as they are poor. The government should provide them education and training so that they can do other valuable work to earn their livelihood. Everyone is equal and deserves to be treated with dignity.
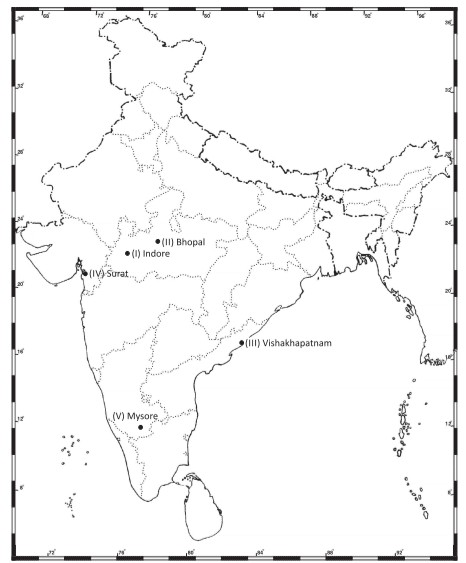
Map Skill
Following is the list of Indian cities that have fared well on cleanliness parameters under the Swachh Bharat Mission. Show these cities on an outline political map of India. Rank Top 5 Cities/States I Indore (MP) II Bhopal (MP) III Vishakhapatnam (AP) IV Surat (Gujarat) V Mysore (Karnataka)
Ans.